Presentation
Once the ecological restoration works have been carried out, the implementation of hydraulic management is necessary. It is used to ensure the preservation of the lagoon habitat but also to create favorable conditions for the nesting of the Pied Avocet and the marsh birds.
For this, each basin is equipped with small hydraulic works allowing precise adjustment of the water levels.
The mudflat structures (first water storage basin) directly connected to the hydraulic network are handled at each high tide (every 15 days) to store water and allow the supply of other basins. Once the upgrades and adjustments of the structures between the basins, the water levels are regularly monitored for possible adjustment according to the defined management methods.
For example, for ponds hosting avocet nesting, a level that is too low can allow terrestrial predators to access the nests, and a level that is too high will cause the nests to drown. Great vigilance is therefore necessary, especially during periods of high evaporation (May to July), during heavy rains or high tides.
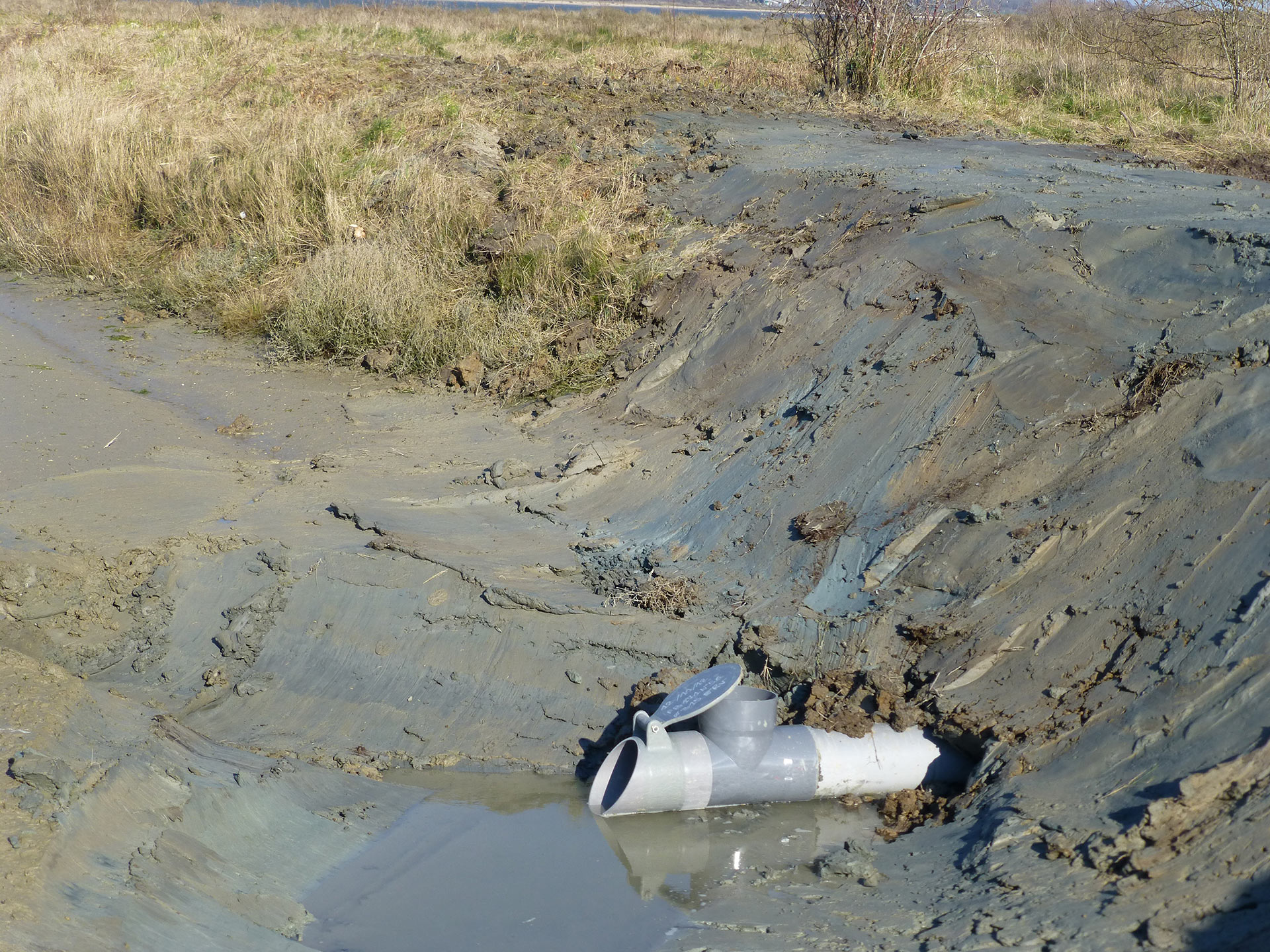

Hatch and pipe without adaptation (photo credit: Cap Atlantique)
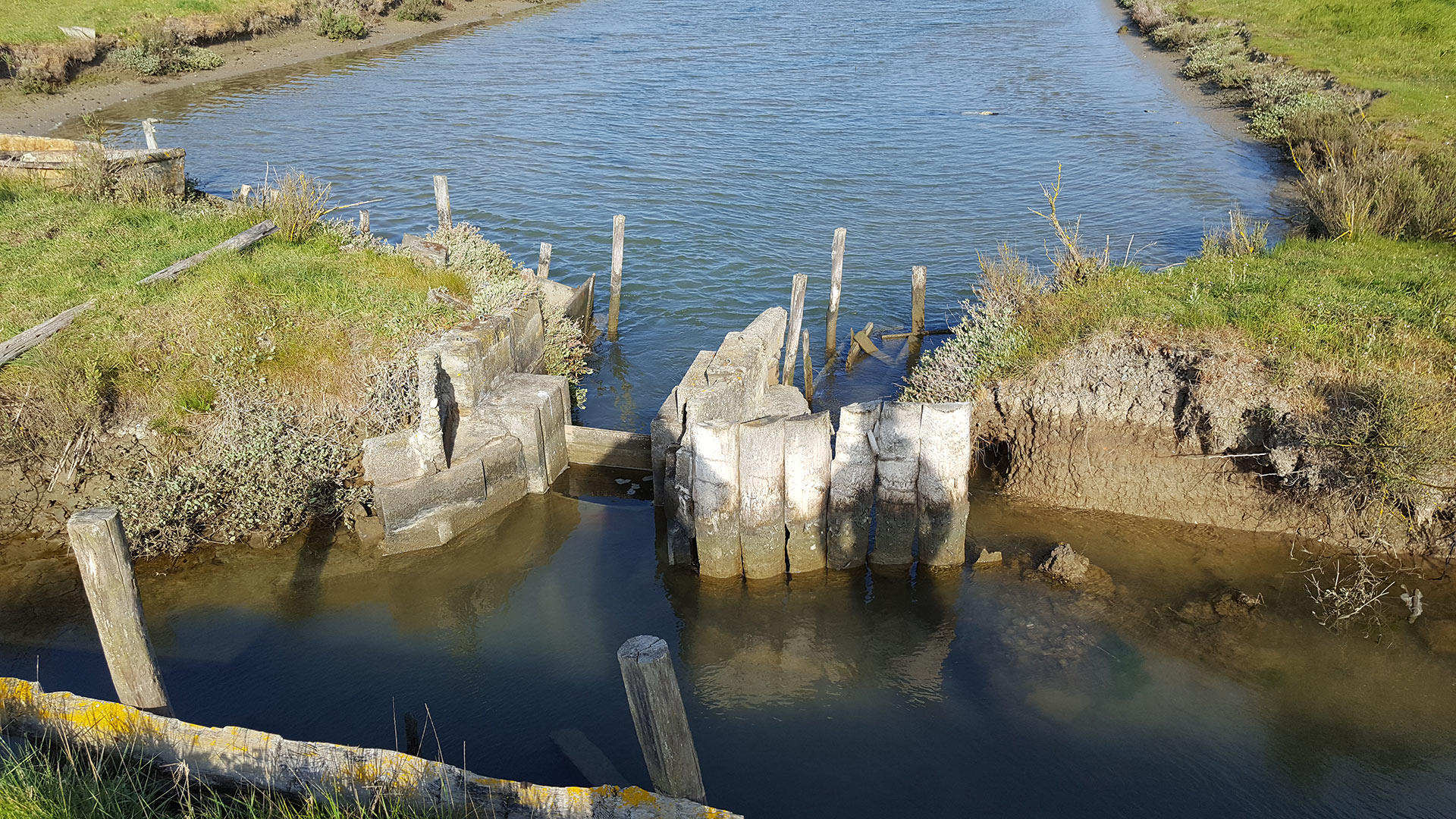

Eraille: traditional work of Île de Noirmoutier (photo credit : CCIN)
Depending on the biological challenges present, different hydraulic management rules can be implemented in the LIFE Sallina basins to promote:
- Salted seagrass (Ruppia sp.).
- Brackish seagrass (Buttercup of Baudot-Ranunculus baudotii, etc…).
- Characeae meadows (Tolypelle saline-Tolypella salina, Lampropthamnium papulosum, etc.)
- Nesting of the Avocet elegant (Recurvirostra avosetta) and feeding the chicks.
- The development of reed beds or bulrushes.
Hydraulic management is carried out in consultation with riparian operators and other users of the marsh to ensure the compatibility of the management carried out under LIFE Sallina with their activities (salt production, hunting).
Hydraulic management is carried out by the LIFE Sallina team or by salt workers. As part of this mission, the agents may be required to carry out routine maintenance work (unblocking, cleaning) to allow the proper functioning of the works.
Goals
Installation of approximately 200 structures and management of approximately 300 structures
Development of seagrass beds according to the different methods of hydraulic management
In case of nesting, optimal management of water levels to avoid drowning of nests and allow feeding of chicks.
Advancement
Action carried out throughout the year on the basins which have been the subject of restoration work.
Résultats
- Suivi habitat lagunaire
- suivi avocette